

Chapter 2 Understanding Transactions and Component Lifecycles
EAServer includes CORBA Object Transaction Service (OTS) and X/Open architecture (XA) as one of its distributed transaction models. EAServer uses the Transarc Encina® transaction coordinator to manage OTS/XA transactions. You can define components, and component methods so that the transaction coordinator automatically handles transactions (called implicit control). You can also write code in the component or client to manage transactions (called explicit control).
![]() EAServer does not currently support nested OTS/XA
transactions (also called subtransactions). If a method attempts
to create a subtransaction, the SubTransactionUnavailable exception
is raised.
EAServer does not currently support nested OTS/XA
transactions (also called subtransactions). If a method attempts
to create a subtransaction, the SubTransactionUnavailable exception
is raised.
Two-phase commit ensures that all changes to recoverable resources (for example, multiple database servers) occur atomically, and the failure of any resource to complete causes all other resources to undo changes. Two-phase commit consists of a prepare phase and an execution phase. In the prepare phase, the transaction coordinator validates that all resources are available. In the execution phase, the transaction coordinator executes all updates to the resources.
An OTS/XA transaction coordinator uses XA resources to manage transactions. An XA resource manages information using an XA-compliant interface, for example, a database server or IBM's MQSeries® (a message queueing system). The XA interface standard is an element of the X/Open Distributed Transaction Processing (DTP) model. Currently, Sybase provides an XA-compliant interface through CT-Lib. In addition, EAServer provides jConnect, which is a JTA (Java Transaction API)-compliant JDBC driver. See the EAServer System Administration Guide for more information about managing XA resources.
A component with the OTS-Style transaction attribute enabled follows the standard component lifecycle as described in "Component lifecycles".
Generally, OTS transactions behave in the same way as described in "EAServer's transaction processing model". However, C++ clients as well as C++ components can explicitly start OTS transactions. When a client explicitly starts a transaction, a component method can be in the client-initiated transaction, start a new transaction, or does not have to be in any transaction at all, depending on the component transaction attribute's setting. Inappropriate transaction settings may result in runtime errors. For more information about component transaction attributes, see "Transactional component attribute". Also see "Managing explicit OTS transactions" for specific information about coding explicit OTS transactions.
![]() You can choose OTS Style or Bean Managed for a C++ component's transaction
attribute and still use the Current interface
to explicitly start transactions.
You can choose OTS Style or Bean Managed for a C++ component's transaction
attribute and still use the Current interface
to explicitly start transactions.
When EAServer runs in OTS/XA or JTS mode, it can share the transaction coordinator across multiple servers. If a transactional component on one server invokes a component method on another server, both components can participate in the same transaction. Also, a client can invoke components on multiple servers that all participate in the same transaction. This feature is useful for load balancing.
The OTS/XA transaction coordinator enables you to manage remote transactions using the CosTransactions interface. For more information, see "Transaction coordinators".
Figure 2-4 illustrates a scenario in which a client calls a component method on server A, which calls a component method on server B. Server A and server B use different databases. To ensure that all the database updates occur within the scope of a single transaction, EAServer passes the transaction context between servers.
Figure 2-4: Transaction interoperability
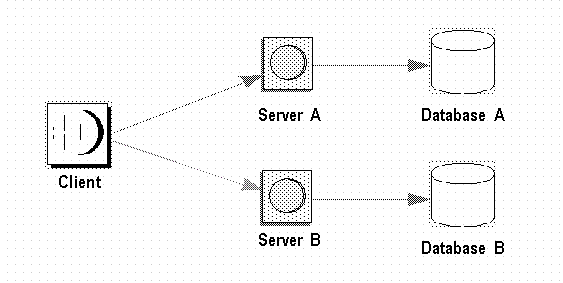
Figure 2-5 illustrates an example where a client calls components on multiple servers, which all participate in the same transaction. The client manages the transaction by calling component methods on each server and passing the transaction context.
A 3.6.x client that uses the javax.transaction.UserTransaction interface cannot run with EAServer version 4.0 or later. The IIOP message structure has changed for clients that use this interface, resulting in version incompatibility. Likewise, a 4.0 or later client cannot run with a 3.6.x server.
The Java Transaction Service (JTS) Transaction Manager implements the specifications for the Java Transaction API (JTA) 1.0 and the OMG Object Transaction Service 1.1. The JTS Transaction Manager enables EAServer to control the scope and duration of transactions across multiple resource managers. It also provides the ability to synchronize transactions and to communicate with other transaction managers using CORBA OTS. The JTS/JTA transaction model specifies that a transaction may exist without any connections. Connections and resources are dynamically enlisted into a transaction when they are requested.
EAServer implements the javax.transaction.TransactionManager interface, which allows it to control transaction boundaries. To manage the interaction between Java and Encina transaction objects, EAServer uses the Java Transaction Manager. Encina continues to act as the primary transaction manager. EAServer's implementation of the javax.transaction.Transaction interface enables it to manage a set of javax.transaction.xa.XAResource resources that participate in a transaction. To determine the boundaries and outcome for these transactions, EAServer uses the CosTransaction::Resource interface.
![]() Configuring EAServer to use JTS/JTA transactions
Configuring EAServer to use JTS/JTA transactions
| Copyright © 2002 Sybase, Inc. All rights reserved. |

| |